Introduction
 The Iron Bridge is the star attraction of the Ironbridge area, the focal point of the UNESCO World Heritage Site (awarded in 1986), and managed since 1991 by the Severn Gorge Countryside Trust, which includes 52 sites, 60 historic structures, 230 hectares of woodland, 25 acres of wild flower meadow, 26kms of paths and 8 kms of bridleways. This includes at least twelve museums and managed sites, some of which are open all year round, others only seasonally. This makes the Ironbridge Gorge a splendid place for an extended visit as well as for day trips to selected destinations.
The Iron Bridge is the star attraction of the Ironbridge area, the focal point of the UNESCO World Heritage Site (awarded in 1986), and managed since 1991 by the Severn Gorge Countryside Trust, which includes 52 sites, 60 historic structures, 230 hectares of woodland, 25 acres of wild flower meadow, 26kms of paths and 8 kms of bridleways. This includes at least twelve museums and managed sites, some of which are open all year round, others only seasonally. This makes the Ironbridge Gorge a splendid place for an extended visit as well as for day trips to selected destinations.
It can be easy to come away with a fragmented view of Ironbridge Gorge whilst driving between the bridge and the different museums and villages. Once known collectively as Coalbrookdale, the immediate valley area is now divided into Ironbridge, Jackfield, Coalport and Coalbrookdale with outlying attractions in the surrounding area. However, all areas are united by the underlying geology that was revealed by glacial action and became the source of raw materials for manufacturing in the area, both of ironworks that produced industrial scale projects like the bridge itself as well as decorative objects for home and office; and clay-based household objects such as tiles, and finer decorative china.
The first engineer and entrepreneur to exploit the full potential of the Ironbridge area’s geology for industry was Abraham Darby I who had a small furnace in the area and who in 1709 successfully experimented with carbonized coal, called coke, as fuel instead of charcoal that depended on less volumes of mature woodlands and required much less labour. Abraham Darby I’s formula for iron was a ratio of 600kg coke to 600kg of ironstone and 250g limestone, all of which were available locally, and produced 250kg iron. Efficiencies in the iron manufacturing industry were further improved with refinement of coke production and the introduction of steam-powered engines later in the 18th century.
==
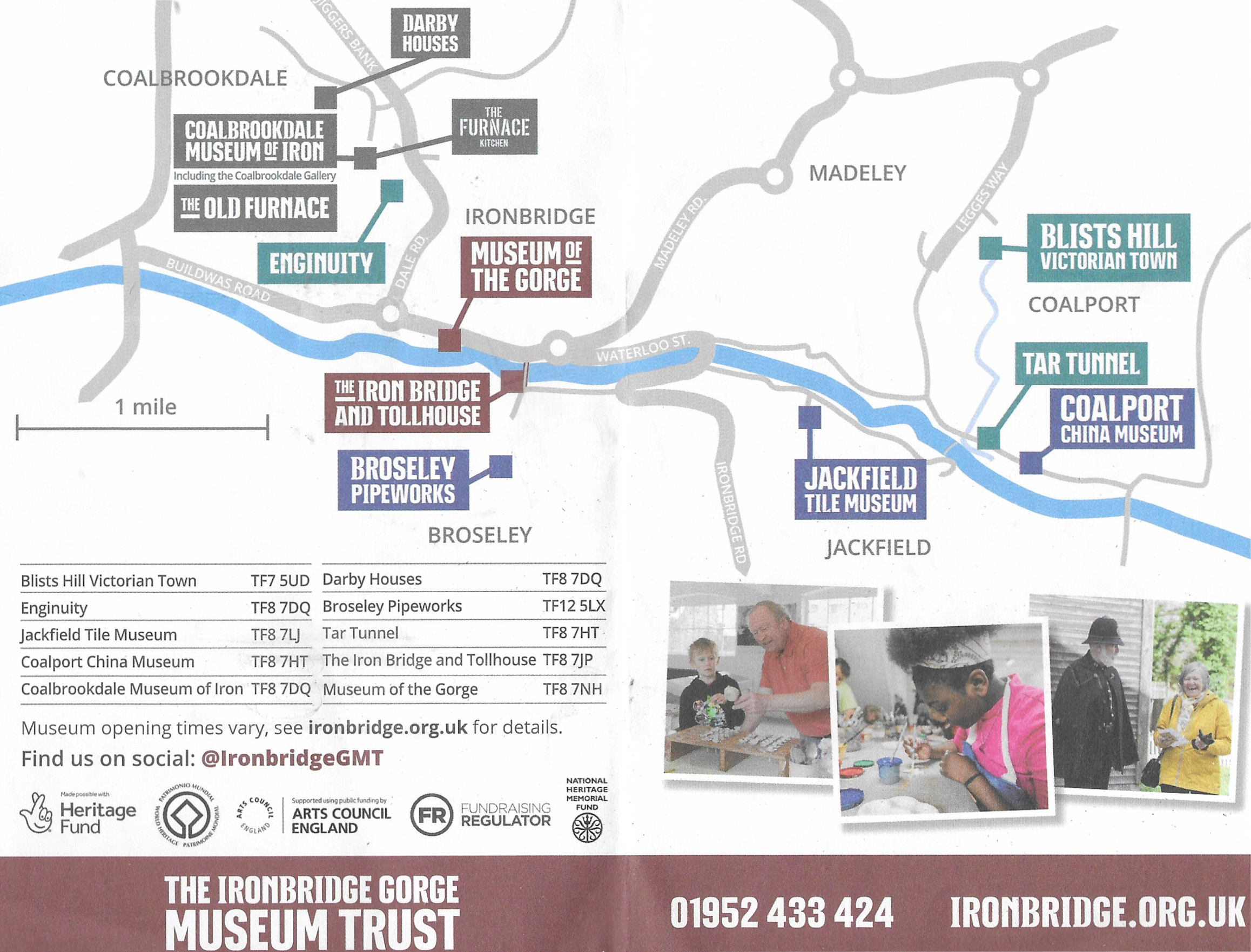
From the leaflet “Exploring Ironbridge Gorge” showing the key components of the visitor attractions today
 The other essential geographical feature was the river Severn, which flows through the Ironbridge Gorge. The gorge was itself formed by the pressure from a glacier, that sat over much of Shropshire, on the underlying trapped water. This water, with nowhere else to go, forced itself out from under the glacier through the soft limestone of what are now named Benthall Edge and Lincoln Hill, forming the steep-sided channel that the river occupies today. In the 18th and 19th centuries the water from the Severn provided both power, first to water wheels and then steam engines, as well as cooling for many of the machines and as part of many of the industrial processes. It was also a major transport link between the Ironbridge area, the Bristol Channel and the rest of the world. Looking at the river today in its wildlife and heritage setting, it is difficult to imagine how much pollution there must have been both in the air and in the water, produced by the furnaces, forges and kilns, as well as the chemical waste.
The other essential geographical feature was the river Severn, which flows through the Ironbridge Gorge. The gorge was itself formed by the pressure from a glacier, that sat over much of Shropshire, on the underlying trapped water. This water, with nowhere else to go, forced itself out from under the glacier through the soft limestone of what are now named Benthall Edge and Lincoln Hill, forming the steep-sided channel that the river occupies today. In the 18th and 19th centuries the water from the Severn provided both power, first to water wheels and then steam engines, as well as cooling for many of the machines and as part of many of the industrial processes. It was also a major transport link between the Ironbridge area, the Bristol Channel and the rest of the world. Looking at the river today in its wildlife and heritage setting, it is difficult to imagine how much pollution there must have been both in the air and in the water, produced by the furnaces, forges and kilns, as well as the chemical waste.
The Iron Bridge
 The building of a cast-iron bridge was proposed by Thomas Farnolls Pritchard 1723-1777), who also designed the prototype. Up until the building of the bridge, which opened in 1781, most of the traffic across the river was by ferry; the nearest bridge was the medieval Buildwas bridge next to Buildwas abbey, 3.8km upstream from the site of the new Iron Bridge. The connection between the north and south sides of the river was essential, allowing the movement of raw materials, people and supplies. The bridge was an obvious solution to the problem of a river that was vulnerable to changing levels and seasonal weather extremes such as low levels, floods and high winds.
The building of a cast-iron bridge was proposed by Thomas Farnolls Pritchard 1723-1777), who also designed the prototype. Up until the building of the bridge, which opened in 1781, most of the traffic across the river was by ferry; the nearest bridge was the medieval Buildwas bridge next to Buildwas abbey, 3.8km upstream from the site of the new Iron Bridge. The connection between the north and south sides of the river was essential, allowing the movement of raw materials, people and supplies. The bridge was an obvious solution to the problem of a river that was vulnerable to changing levels and seasonal weather extremes such as low levels, floods and high winds.
Thomas Farnolls Pritchard specialized in the restoration of prestigious houses. Although he had built bridges in wood and stone, none had been as ambitious as his Ironbridge proposal, and this was the first attempt to use cast iron to span a gap this wide. the idea was to use a single arch to span the widest section of the river, avoiding piers that would impede navigation. He sent his proposal for a cast iron bridge to John “Iron-Mad” Wilkinson, an obvious sponsor for this type of innovative project. Wilkinson in turn discussed the matter with Abraham Darby III, who instantly saw the potential for the bridge not merely as a means of spanning the river, but of marketing his company and the benefits of the Ironbridge area as a whole, at that time known collectively as Coalbrookdale. A committee was formed to take the project forward.

The only known image of the bridge under construction, by Elias Martin (1739-1818) painted in the summer of 1779
An Act of Parliament was granted in 1776, and shares were soon issued to raise funds. Work began in 1777. The iron for the bridge was cast by Darby at his works, but there is no record as to which of his three furnace sites was responsible. It is probable that the work was shared out to all three, spreading the load to ensure that existing and new commercial contracts continued to be delivered. It is known that wooden scaffolding was employed in the construction of the iron bridge, but the exact process of construction is unrecorded. The painted inscription on the ironwork that spans the top of the bridge reads “This bridge was cast at Coalbrook-Dale and erected in the year MXDCCLXXIX [1779].” Ribs were cast in two pieces and joined in the middle. Observation of the bridge’s construction shows that it was assembled using both metalwork techniques and joinery techniques such as mortise and tenon joints and dovetailing. The ironwork was flanked by and set into stone abutments.
 Once the basic frame was built, spanning 100ft 6ins (c.31m) the scaffolding was removed in 1779 and a road was constructed over the top and a small toll-house added on the southern side. The bridge eventually opened in 1781, on New Year’s Day. Although it was built closely in the spirit of Pritchard’s original plan, several changes were made. Pritchard did not live to see the bridge completed but his family were duly paid for his contribution.
Once the basic frame was built, spanning 100ft 6ins (c.31m) the scaffolding was removed in 1779 and a road was constructed over the top and a small toll-house added on the southern side. The bridge eventually opened in 1781, on New Year’s Day. Although it was built closely in the spirit of Pritchard’s original plan, several changes were made. Pritchard did not live to see the bridge completed but his family were duly paid for his contribution.
The bridge had cost a massive £6000, twice the estimate. Darby had taken on the bulk of this financial burden. Although he was quick to use the marketing potential of the bridge deploying it as an advertising emblem, and visitors came from all over the world to see it, neither this nor the tolls for use of the bridge were able to make up the substantial shortfall. Darby was unable to make up his losses and the bridge left him in debt for the rest of his life, with both business and properties mortgaged.
Unlike Buildwas and other Severn bridges, the Iron Bridge survived the Great Flood of 1795, unlike the medieval stone Buildwas Bridge, proving the durability of a cast iron bridge. Thomas Telford had repaired the Buildwas bridge in 1779 but during 1795 it was damaged beyond repair and, taking Ironbridge as his model, Telford replaced it with his own iron bridge.
Over the following century repairs were carried out as required, but during the early 20th century its stability was questioned and its demolition was suggested in 1926. Fortunately, it was decided to save the bridge and was limited to pedestrian use from 1934, and was listed as a National Monument. In 1950 it passed into the hands of Shropshire County Council. Substantial restoration work has been carried out since 1972 to stabilize and reinforce the bridge. It is now in the care of English Heritage.

A footpath runs under the bridge on the Ironbridge village side, allowing a good view of some of the metalwork.
The small town of Ironbridge began to develop in the later 18th century. Today Ironbridge village is small but attractive, with a row of shops, cafes and pubs lining the road that runs along Severn between Ironbridge and Coalbrookdale, with houses, a massive church and other community buildings climbing the hill above the river in Ironbridge. I can recommend the ice cream 🙂
The Museums
I have already posted about the glorious Jackfield Tile Museum here, with lots of photos, but there are at least total of twelve museums and related visitor attractions in the Ironbridge area, and I will post about the other four museums that I visited on future posts. I would have visited the Broseley Pipeworks and the Tar Tunnel, but neither were open, so I plan to visit those when they re-open. The Darby Houses were also closed. Nor did I visit Enginuity, which appears to be geared towards children, but actually looks like a lot of fun, if you are child-friendly, with plenty of interactive activities demonstrating engineering principals. Blist’s Hill Victorian Town just wasn’t my cup of tea, but the recreation of everyday life in 1900 Shropshire sounds like a good initiative.
==
A have talked about the Jackfield Tile Museum in detail on a previous post. Don’t miss it. In the world of museums, this is a rock star.
The Coalport China Museum to the east of of Ironbridge and Jackfield consists of two areas of interest – the displays of decorated china ware made in the local area, and the surviving furnaces in which many of them were made, which you can enter and walk around. Although the china is worth seeing, partly because it demonstrates the many shapes, textures and patterns that were produced, I found the splendid industrial heritage of this site the most evocative and engaging part of the experience, bringing the sheer vast materiality of these enterprises to life. This part of the Severn valley would have been full of these furnaces. There is good car parking. Ticket prices are on the Ironbridge website, and don’t forget to ask for an English Heritage discount if you are a member.
The Toll House, free of charge, is set just to the south of the Ironbridge near to the car park, is now a museum of the bridge, telling it story. This is mainly a matter of information boards rather than objects on display, but is very informative. It also serves as a ticket office for those wishing to buy family tickets and day passes (although you can also buy tickets on an ad hoc basis when you visit individual museums).
To the east, easily reached by walking along the wide pathway that follows the Severn, is the Museum of the Gorge, also free of charge. There is a small car park next to it. The exterior of the building is fabulous, and there are some great internal features, and there are information boards about the history of the building and the conservation work, as well as a selection of reproductions of historic maps of Shropshire.
Up the hill is the splendid Coalbrookdale Museum of Iron. The museum captures the essence of the area’s iron production output, from geology and early history via the bridge itself, including some excellent original images of the Ironbridge, via civil engineering equipment to a surprising and elaborate array of domestic items. On the museum site is also the substantial and impressive remains of the the Old Furnace, some of which has been turned into an indoor feature. Like the China Museum, this is a splendid mix of museum displays and well preserved and explained industrial archaeology.
Not shown on the above map is the Bedlam furnace, half way between Jackfield and Iron bridge on the north side of the river, which can be viewed from the laybay in front of it and is well worth visiting, partly because although there is little of it left, it was the subject of Philip de Loutherberg’s famous 1801 painting.

“Coalbrookdale by Night” by Philippe Jacques de Loutherbourg, 1801. Open coke hearths give off vivid flames and smoke. Archetypal image of the Industrial Revolution. From a colour transparency in the Science Museum Photographic Archive, CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 Licence.
Visiting
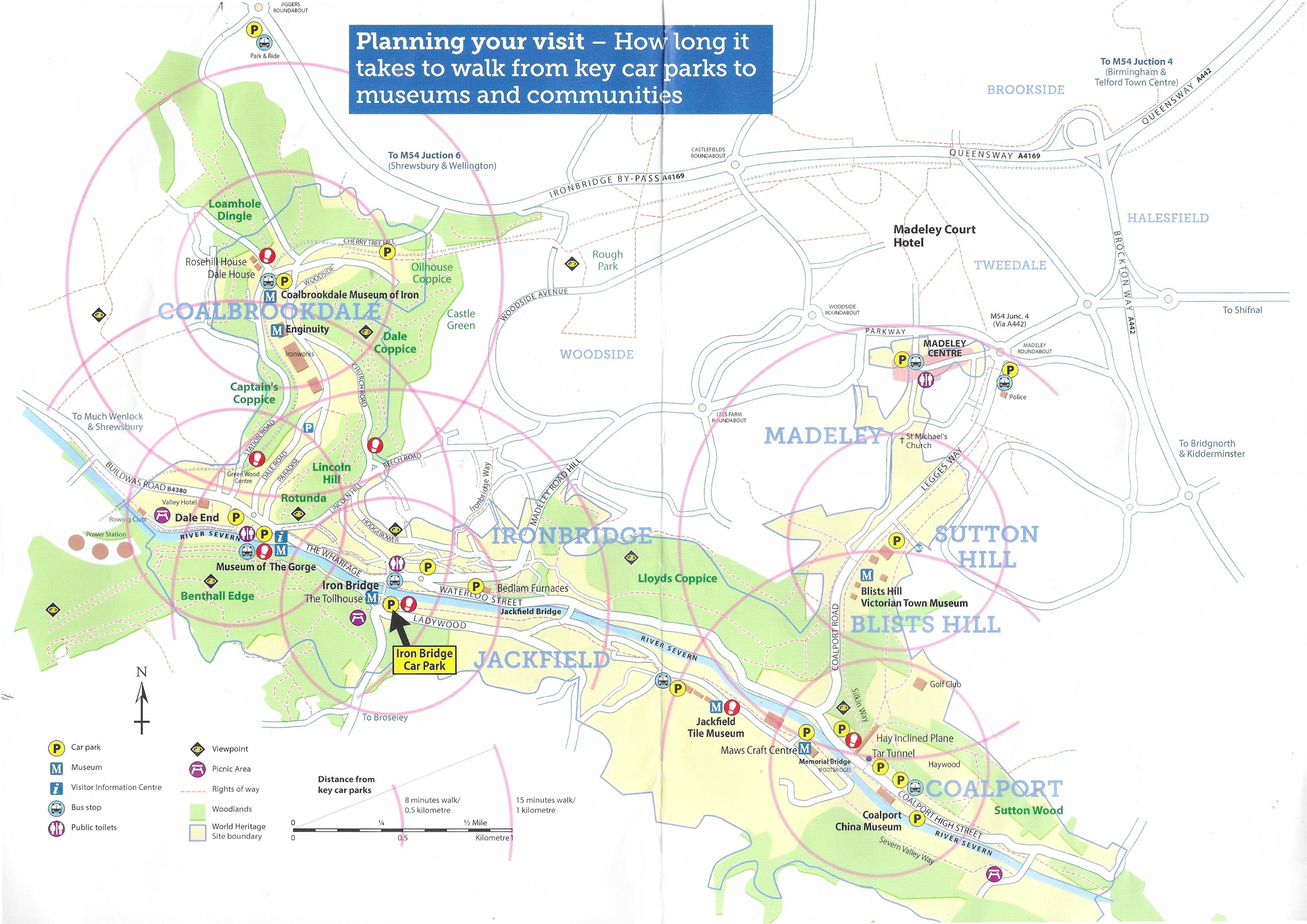
Wherever you are, keep an eye open for leaflets, as some of these have some very helpful information, including chronological charts, maps and self-guided trails to some of the features that are beyond the museums.
The bridge
 The bridge is open to visitors all year round, assuming that no restoration or repair work is taking place. The opening times for the toll house, which acts as a museum for the bridge, can be found on the Ironbridge Gorge website. Extensive pay and display parking for Ironbridge is available on the south side of the river, which allows you to choose how long you are going to stay. This is handy if you just want to spend a short time looking at the bridge and browsing in the village but also allows you to stay longer if you want to walk along to to Coalbrookdale to visit the Museum of the Gorge museum and up the shallow hill to visit Enginuity and the Coalbrookdale Museum of Iron.
The bridge is open to visitors all year round, assuming that no restoration or repair work is taking place. The opening times for the toll house, which acts as a museum for the bridge, can be found on the Ironbridge Gorge website. Extensive pay and display parking for Ironbridge is available on the south side of the river, which allows you to choose how long you are going to stay. This is handy if you just want to spend a short time looking at the bridge and browsing in the village but also allows you to stay longer if you want to walk along to to Coalbrookdale to visit the Museum of the Gorge museum and up the shallow hill to visit Enginuity and the Coalbrookdale Museum of Iron.
The museums
All the Ironbridge Gorge museums are covered on one website – Ironbrige Valley of Invention. This inexplicably has very few images of what’s on display, and suffers from Russian doll syndrome, with pages buried within pages, but the information on days when the museums are open and closed (changes seasonally) and the opening times are there if you look for them. Some of the museums are closed completely at certain times of the year (such as the Tar Tunnel and the Broseley Tobacco Pipe Works).
Note that if you are a member of English Heritage there is a discount on ticket prices, but you will need to ask for it.
Other sites to visit in the area
This is a rich area for destinations to visit, including five medieval abbeys a relatively short drive away, a number of National Trust properties and only a little further afield, Shrewsbury makes for a rewarding day out with the abbey church, the excellent Shrewsbury Museum and Art Gallery and the attractive medieval and Georgian architecture. Not far away is the RAF Museum at Cosford, just outside Telford (my post about it is here), and whilst there, the Church of St Bartholemew at Tong with its lovely medieval choir, its elaborate tombs and the remarkable Tudor chapel and is crammed full of interest and just a 10 minute drive away.
Sources:
Books, booklets and papers
2019 edition (no author or reference number). Exploring Ironbridge Gorge (booklet). The Ironbridge Gorge Museum Trust Ltd.
Jones, C. 1989. Coal, Gas and Electricity. In (ed.) Pope, R. Atlas of British Social and Economic History Since c.1700. Routledge
Mathias, P. 2001 (second edition). The First Industrial Nation. The Economic History of Britain 1700-1914. Routledge.
Mokyr, Joel 1981 (2nd edition). Technological change 1700-1830. In (eds.) Roderick Floud and Deidre McCloskey, The Economic History of Britain since 1700. Volume 1: 1700-1860. Cambridge University Press
Osborne, R. 2013. Iron, Steam and Money. The Making of the Industrial Revolution. The Bodley Head.
Leaflets
Undated leaflet (no reference number). The Ironbridge and Town. The Ironbridge Gorge Museum Trust Ltd.
Undated leaflet (no reference number). The Iron Trail, Ironbridge Gorge. Severn Gorge Countryside Trust
2024 leaflet (no reference number). Ironbridge Valley of Invention. The Ironbrige Gorge Museum Trust Ltd.
Websites
Ironbridge Valley of Invention
Official website
https://www.ironbridge.org.uk/
UNESCO pages for Ironbridge Gorge
UNESCO World Convention
https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/371/