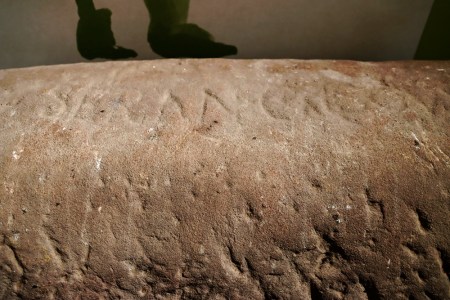A recent Bluesky post by Nina Willburger (drnwillburger.bsky.social) about a 1st century AD Samian ware vessel found in Ladenburg, Germany, repaired in antiquity with lead rivets, reminded me of one of my favourite objects in the Grosvenor Museum in Chester.
It is always a good moment in a museum, especially a small local one, when one looks into a display cabinet and finds something completely unexpected. In the Grosvenor Museum in Chester, there is a high quality Samian bowl that was reconstructed in modern times with deliberately lighter pieces of matt clay added to make it perfectly clear what is old and what is new. What is more interesting is that this elegantly decorated bowl was originally repaired in the Roman period with lead rivets, and this really seizes the attention. It has no label, so there are no details about its date, provenance, history or subject matter, but it appears to show two hunting dogs facing towards each other with a stylized floral motif between them, with other stylized floral and animal forms circling the bowl beneath them. This is a common type of subject matter for Samian ware. Samian (terra sigillata) was the prestige table-ware of the Roman world. It was manufactured between the 1st and 3rd centuries, mainly in Gaul (today parts of France, Belgium and western Germany), and has a distinctive reddish-orange and glossy surface, with a very fine fabric texture. Although Samian could be undecorated, the most prestigious examples featured raised decoration, sometimes showing animal and floral motifs drawn from nature with more elaborate items representing gladiatorial events and simplified narratives drawn from Classical mythology.

Samian sherds from Silchester, a few of dozens rejected by Victorian excavators and thrown onto their spoil heap
Often all that is left of pottery at Roman sites are broken sherds that had been disposed of when a pot was broken. It is a fact of archaeological work that during excavations archaeologists are always in the position of finding the component parts of objects, the broken pieces that once made up a whole item. Today the majority of these are collected and weighed as a source of data about site usage, but in earlier periods of archaeological exploration, smaller and unremarkable sherds were often discarded. More remarkable sherds have always been privileged for collection and recording, as demonstrated by the pages from the excavation report of the Holt tileworks shown below. Where it is clear that sherds belonged to a single vessel attempts might be made to reconstruct the entire vessel, enabling the original appearance of an item to be understood by attempting to restore it to something resembling its original condition. Because of its inherent beauty and complexity, Samian pottery is often the recipient of modern reconstructions. Professor Robert Newstead (1859-1947), curator of the the Grosvenor Museum, was responsible for many of the museum’s reconstructions, using a lighter shade of clay to make it clear that modern repairs had been made.
Fascinatingly, in several parts of the world high value vessels were often repaired during antiquity, enabling broken items to continue in use, although perhaps for a new purpose. In recent years archaeologists and conservationists have shown considerable interest in preserving ancient repairs, recognising them as part of the life-history of an object, and an indication of how such objects were perceived and valued in the past.

Prehistoric repair of a Badarian pot. BM EA62175. Source: British Museum CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
In some parts of the world ancient repairs may date back to prehistoric periods. In around 4400-4000 BC, for example, repairs of bowls of Egyptian prehistoric Badarian ware, a very finely made ceramic belonging to nomadic sheep herders, were often achieved by drilling broken pieces to provide holes that could then bound together with cord, sinew or strips of leather. The Badarian pottery was some of the finest quality ware ever produced in Egypt, requiring considerable artistic flair and manufacturing skill, and was therefore certainly worth repairing.
A ceramic vessel may be broken in many ways at any point during its lifecycle from kiln, via transportation to purchase and usage and finally to breakage. As Angelika Kuettner (Chipstone Foundation) explains:
Whether broken by shipment, cataclysmic weather event, a clumsy servant, a rowdy guest, unsupervised children or animals, or impassioned religious or political zealots, the owner of the ill-fated ceramic object then had to decide whether to repair the dish or dispose of it as waste, as something devalued to the point where it was completely worthless.
The reasons for repairing an item may depend on a number of variables, including such practical considerations as income and geography. Perhaps the owner of the bowl could not afford to purchase a replacement, or there was nowhere nearby to purchase anything similar at the particular time of its breakage. Perhaps the theme had particular significance and nothing equivalent was available locally. As well as practical reasons for a repair, there may have been sentimental reasons attached to a vessel, either because it was connected with a special person or event, perhaps because it was a gift or a family heirloom. It is even possible that the item was discarded by its owner when broken and retrieved by a servant in the household who took the opportunity to repair and own a luxury item. There is no way of knowing what motives were involved in this or any other ancient repair, each one having its own story. In this and other cases it is curious that the repair was so conspicuous, with no attempt at disguise, leading to the appearance of a luxury item being severely compromised.

Lead ingot from a river jetty site at the edge of Chester racecourse dating to 74AD. Source: David Mason’s “Roman Chester. The City of the Eagles,” p.45
The repaired pieces of Samian in the Grosvenor Museum were joined together using lead staples or rivets. As with the Badarian example shown above, the Samian repair technique required holes to be drilled into the object concerned before the rivet or staple could be applied. There is a video at the end that shows how this may have been achieved. Lead was used as a standard building material in Chester, for pipes and as waterproof lining for cisterns and reservoirs, and was mined from places like Halkyn mountain and Meliden near Flint, both in northeast Wales. David Mason estimates that 39 tons or 50 wagon-loads for water pipes, and 34 tons or 43 wagon-loads for reservoir linings were used during the building of Chester. Lead was readily available and would not have been difficult to source for the repair. Research has demonstrated that decorated platters, dishes and bowls are by the the most frequently repaired pieces of Samian in Britain, at both military and civil centres. Unsurprisingly, the number of repairs are highest in remote and upland areas
Another example of Roman repair work in the Grosvenor Museum is is a particularly nice bronze cauldron in the Newstead Gallery, shown right. According to the accompanying label, it was found in Chester’s Roman barracks by Professor Newstead, squashed almost flat, and was found to be made of a single sheet of bronze. Fascinatingly, it had been repaired 14 times during the period of its use, indicating how much it was valued. It was conserved and remounted by York Archaeological Trust in 2009, and looks stunning. As well as this story of ancient repairs this demonstrates a very imaginative and evocative approach to using the remaining parts discovered in an excavation to provide a very evocative reconstruction of the original form.
Repairs of favoured objects have continued to be made throughout history, still to be found sometimes centuries later in people’s homes. Stapling was common in the 19th century for the repair of valued ceramic items like the ornamental dish shown below. Cleverly, the rivets are clearly visible on the underside but do not actually pierce the main surface when turned over.
A more extreme example is this piece of Kutani, obviously very much-loved by its owner judging from the number of rivets used to repair it.

The left hand image shows the multiple staples used in the repair of a Kutani cup, preserving the vessel so that the main design, right, can still be displayed. Photograph by Helen Anderson, with thanks

Kintsugi repaired vessel. Photograph by Haragayato. Source: Wikimedia Commons BY-SA 4.0
Interestingly, in spite of easy access to endless retail products at relatively low cost today, we often choose to repair items that we hold dear or which would cost too much to replace, rather than purchasing new versions. Ceramics are stapled or glued together, like the 19th century dish above, and the now international fashion for a technique called kintsugi (“golden joinery”) pioneered in Japan has given new life to broken objects by combining gold with an adhesive agent to provide a vessel with an entirely new life-force whilst retaining something of its original essence. This has become a skilled craft in its own right, and some kintsugi items now have a unique and precious value of their own. Having had a go at this with a lovely but broken dish that I found in my parents’ loft, I can attest to how much skill is required to produce something both beautiful and functional, skills that I apparently don’t have in any abundance 🙂

The Samian bowl in the Grosvenor Museum, showing both ancient repairs and modern repairs to allow reconstruction and provide a good sense of the original object
The repaired Samian bowl in the Grosvenor Museum, reveals both ancient repairs and modern reconstruction work. Both are part of its life history. There are just as many stories to be found in repaired items as in perfect ones, perhaps more. Although we are often accustomed to seeing only the brightest, best and most complete objects in museum collections, sometimes it is those that were broken and then repaired or otherwise curated by their owners that give us a personal sense of a connection with the past. Archaeology always includes unknowns, and there is never going to be an answer as to why this particular bowl was repaired, but it evokes a sense of the personal in a way that more perfect, undamaged objects in museum collections may not.

Discarded dinner set found in a ditch at Vindolanda on Hadrian’s Wall. Source: Vindolanda Charitable Trust
Vessels that had been repaired, whether lashed, stapled and/or glued would probably never be able to carry liquids without at least some leakage, but they could happily carry dried goods, continue to have decorative and sentimental and even prestige value and to be considered by their owners to retain a useful life.
Just as interesting as all the Samian items that have been repaired, is a single remarkable case of disposal from Vindolanda, which engagingly provides evidence of one of the biggest temper-tantrums recorded in British archaeology. The Vindolanda Charitable Trust website explains:
In our Museum at Vindolanda we have an almost complete dinner set of Samian Ware which was imported from the famous La Graufesenque potteries (near the modern French town of Millau at the southern end of the Gorges du Tarn). Using the potters stamps we have dated this collection to the late AD80s. The pottery had been broken in transit and was thrown, unused, into the ditch of the fort. . . . Imagine how disappointing it would be to finally get your delivery only for it to be broken!
It puts breakages received from Amazon into perspective.
xxx

Professor Newstead and some of his restored Samian items, in the Newstead Gallery of the Grosvenor Museum.
At the end of the post see a nice video by Guy de la Bédoyère who, amongst other things, discusses the variable quality of Samian found in Britain and elsewhere; and another one that shows how, in the Roman period, mending holes may have been made in Samian using a manual drill that uses a simple but effective technology deriving from the use of spindle whorls.
Sources:
Books and papers
Albert, Kasi 2012. Ceramic rivet repair: History, technology, and conservation approaches. Studies in Conservation, 57(sup1), S1–S8.
Hsieh, Julia 2016. The Practice of Repairing Vessels in Ancient Egypt. Methods of Repair and Anthropological Implications. Near Eastern Archaeology, Vol. 79, No. 4 (December 2016), pp. 280-283
Dooijes, Renske and Olivier Nieuwenhuyse 2007. Ancient Repairs: Techniques and Social Meaning. In (eds): M. Benz and U. Kästner (red.), Konservieren oder restaurieren, die Restaurierung griechischer Vasen von der Antike bis heute (3rd suppl. to the CVA Germany), Beck Publishers, 15-20
https://www.academia.edu/13881341/Ancient_repairs_techniques_and_social_meaning
Garachon, Isabelle 2010. Old Repairs of China and Glass. Rijksmuseum Bulletin, 15th March 2010., Vol. 58 No.
https://www.academia.edu/10120934/Old_repairs_of_China_and_glass
Gosden, Chris and Yvonne Marshall 1999. The Cultural Biography of Objects. World Archaeology 31(2), October 1999, p.169-178
Grimes, W.F. 1930. Holt, Denbighshire: Twentieth Legion at Castle Lyons. Y Cymmrodor. Society of Cymmrodorion.
Kopytoff, Igor 1986. The cultural biography of things: commoditization as process. In (ed.) Arjun Appadurai. The Social Life of Things. Commodities in cultural perspective. Cambridge University Press
Mason, David J.P. 2001, 2007. Roman Chester. The City of the Eagles. Tempus Publishing
Ramakers, Hanneke 2013. Historic Repairs. Conservation Journal Autumn 2013 Issue 61
http://www.vam.ac.uk/content/journals/conservation-journal/spring-2013-issue-61/historic-repairs/
Willis, Steven 2004 Samian Pottery, a Resource for the Study of Roman Britain and Beyond: the results of the English Heritage funded Samian Project. An e-monograph. Internet Archaeology 17.
https://intarch.ac.uk/journal/issue17/willis_toc.html
Chapter 11, 1-7 – Samian Repaired
https://intarch.ac.uk/journal/issue17/1/11.1_2.html
Websites
BlueSky – Dr Nina Willburger
Fascinating glimpse into everyday Roman life
https://bsky.app/profile/drnwillburger.bsky.social/post/3m73bxsbs4k2n
Chipstone Foundation
Simply Riveting: Broken and Mended Ceramics by Angelika R. Kuettner, 2016
https://chipstone.org/images.php/742/Ceramics-in-America-2016/Simply-Riveting:-Broken-and-Mended-Ceramics
Field Museum
Restoring Pottery
https://www.fieldmuseum.org/science/research/area/conserving-our-collections/treatment/restoring-pottery
Alice T. Miner Museum
Conserving the Collection: Ceramic Repair Techniques by Ellen E. Adams, Thursday, August 26, 2021
http://minermuseum.blogspot.com/2021/08/conserving-collection-ceramic-repair.html
Vindolanda Charitable Trust
A Closer Look at Samian Pottery
https://www.vindolanda.com/blog/a-closer-look-at-samian-pottery